-
أخر الأخبار
- استكشف
-
المدونات
Understanding Osteoarthritis (OA): Causes, Symptoms, and Management
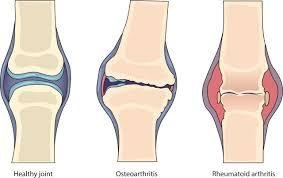
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, affecting millions of people worldwide. Often referred to as “wear-and-tear” arthritis, it develops when the protective cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones gradually breaks down. While OA is more common with aging, it is not simply a disease of old age—lifestyle, genetics, and injury also play important roles. Understanding the condition, its symptoms, and management options can help people live more comfortably and maintain mobility.
Carticlas tablets are a cutting-edge dietary supplement formulated to promote joint health, reduce inflammation, and support overall well-being. They are designed to address the common issues associated with aging, high physical activity, and other factors that affect joint and bone health.
What Is Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis is a chronic joint condition in which the cartilage, the smooth tissue covering the ends of bones, wears away over time. Without this cushioning, bones rub against each other, leading to pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced joint flexibility. OA can affect any joint but most commonly occurs in the knees, hips, hands, and spine.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of osteoarthritis:
-
Age: The risk increases as cartilage naturally wears down over time.
-
Genetics: A family history of OA can make someone more prone to the condition.
-
Joint injury: Sports injuries, fractures, or repetitive stress on joints can increase the risk.
-
Obesity: Extra body weight puts additional strain on weight-bearing joints like the hips and knees.
-
Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop OA, especially after menopause.
-
Occupation: Jobs that involve repetitive motion or heavy lifting can increase wear on certain joints.
Symptoms of Osteoarthritis
OA symptoms usually develop gradually and worsen over time. Common signs include:
-
Joint pain during or after movement
-
Stiffness, especially in the morning or after periods of inactivity
-
Tenderness when pressing near affected joints
-
Loss of flexibility and reduced range of motion
-
Grating sensation or popping sounds when moving the joint
-
Bone spurs (small bony growths) that may form around the joint
These symptoms can vary in severity, with some people experiencing only mild discomfort while others face significant mobility challenges.
Diagnosis
Doctors typically diagnose OA through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and imaging tests. X-rays can reveal joint damage such as narrowing spaces and bone spurs, while MRIs may provide more detailed images. Blood tests are sometimes used to rule out other conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
Management and Treatment Options
While there is no cure for osteoarthritis, treatments focus on relieving pain, improving function, and slowing progression.
Lifestyle and Self-Care
-
Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on joints.
-
Exercise: Low-impact activities like swimming, cycling, and walking strengthen muscles around joints, improve flexibility, and reduce stiffness.
-
Physical therapy: Targeted exercises can enhance mobility and ease discomfort.
-
Assistive devices: Braces, canes, or shoe inserts may help reduce strain.
Medications
-
Pain relievers: Over-the-counter options like acetaminophen or NSAIDs (ibuprofen, naproxen) can help.
-
Topical treatments: Creams and gels with anti-inflammatory properties may provide local relief.
-
Prescription options: In more severe cases, stronger medications may be prescribed.
Medical Procedures
-
Injections: Corticosteroid or hyaluronic acid injections may offer temporary pain relief.
-
Surgery: For advanced OA, joint replacement surgery (such as knee or hip replacement) may restore mobility and improve quality of life.
Living With Osteoarthritis
OA can be challenging, but lifestyle adjustments make a big difference. Practicing joint-friendly activities, maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, managing stress, and using heat or cold therapy can ease daily discomfort. Support from healthcare providers, physical therapists, and arthritis support groups can also provide valuable guidance and encouragement.
Conclusion
Osteoarthritis is a common but manageable condition that affects joint health and quality of life. By recognizing symptoms early and adopting lifestyle changes alongside medical treatments, individuals can slow its progression, relieve pain, and maintain an active lifestyle. With the right strategies, living well with osteoarthritis is entirely possible.






